What is Hypothyroidism?
Commonly referred to as an underactive thyroid, hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland doesn’t produce sufficient hormones, leading to a slowdown in various bodily functions. Hypothyroidism is a disorder of the endocrine system which is responsible for the secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Understanding Hypothyroidism
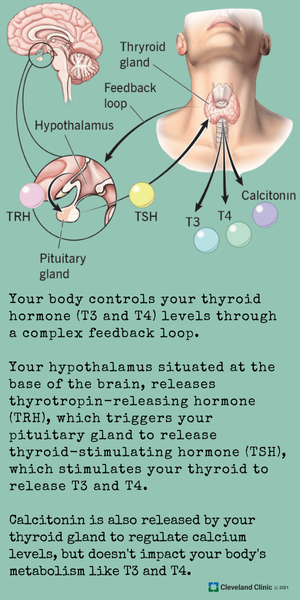
The thyroid gland regulates growth, development and metabolism by using iodine and converting it into triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Numbers 3 and 4 refer to the number of atoms of iodine in each hormone. Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, and humans need about 150 mcg (millionths of a gram) each day. More T3 and T4 hormones circulating in the blood equate to a faster metabolism, whilst lower amounts result in a reduced metabolism.
The thyroid is controlled by the pituitary gland, which is situated at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in response to T3 and T4 hormone levels. When there is too little T3 and T4 being released by the thyroid, the pituitary increases the amount of TSH produced, signalling the thyroid to produce more hormone. If iodine levels are too low, even though the gland will compensate for mild to moderate deficiency at the cost of the thyroid being stimulated and enlarged, eventually hormone levels drop, and hypothyroidism occurs.
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall growth through hormone secretion. When it underperforms, it can result in symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, depression, and sensitivity to cold. From a naturopathic perspective, managing hypothyroidism involves a holistic approach that addresses the cause of hypothyroidism and supports the body’s natural healing processes.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Several factors can contribute to this condition, including autoimmune disorders, nutrient deficiencies, medical treatments, and congenital conditions.
Autoimmune Disorders
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: The most common cause of hypothyroidism, this autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and reduced hormone production.
- Atrophic Thyroiditis: A less common autoimmune condition where the thyroid gradually shrinks and loses function.
Iodine Deficiency or Excess
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. A lack of dietary iodine can lead to hypothyroidism and goitre (thyroid gland enlargement).
- Excess Iodine Intake: While iodine is necessary, too much iodine (from supplements, medications, or excessive seaweed consumption) can suppress thyroid function.
Of note: Iodine deficiency is the major cause of hypothyroidism worldwide in iodine-deficient areas. In iodine-replete areas such as Australia, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the major cause of hypothyroidism.
Thyroid Surgery or Radiation Therapy
- Thyroidectomy: Partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland due to nodules, cancer, or hyperthyroidism can result in hypothyroidism.
- Radiation Treatment: Radiation therapy for head, neck, or thyroid cancer, as well as radioactive iodine treatment for hyperthyroidism, can lead to hypothyroidism.
Congenital Hypothyroidism (Present at Birth)
- Some infants are born with an underactive thyroid due to genetic mutations or improper thyroid gland development. If untreated, this can lead to developmental delays and growth issues.
Certain Medications
- Lithium (used for bipolar disorder), Amiodarone (a heart medication), Interferon-alpha and IL-2 (used for cancer or viral infections), as well as Anti-thyroid drugs (used for hyperthyroidism, which can sometimes overcorrect thyroid function), can impact the thyroid gland and its production of hormones.
Pituitary or Hypothalamic Disorders
- The pituitary gland produces Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which signals the thyroid to produce hormones. If the pituitary gland is damaged (due to tumours, injury, or disease), it may fail to stimulate the thyroid properly. Disorders of the hypothalamus, which regulates pituitary function, can lead to hypothyroidism.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Signs and symptoms can vary depending on the cause and the severity, but commonly include:
- General Changes
-
- Fatigue and low energy
- Unexplained weight gain
- Cold intolerance (feeling cold even in warm temperatures)
- Puffy face and swelling (especially in the hands, feet, and around the eyes)
- Skin, Hair, and Nail Changes
- Dry, rough, or pale skin
- Thinning or brittle hair
- Hair loss (especially from the scalp and outer eyebrows)
- Brittle or slow-growing nails
- Mental and Emotional Symptoms
- Depression or mood changes
- Brain fog, forgetfulness, or difficulty concentrating
- Slower thinking or difficulty processing information
- Metabolic and Digestive Symptoms
- Slow metabolism leading to constipation
- Hoarseness or deepened voice
- Fluid retention and bloating
- Associated with the development of metabolic syndrome
- Cardiovascular Symptoms
-
- Slow heart rate (bradycardia)
- High cholesterol levels lead to atherosclerotic disease and an increased prevalence of ischaemic heart disease
- Poor circulation, resulting in cold hands and feet
- High homocysteine is associated with atrial fibrillation, decreased cardiac output and diastolic hypertension
- Muscle and Joint Symptoms
- Muscle weakness or cramps
- Joint pain or stiffness
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Reproductive and Hormonal Symptoms
- Irregular or heavy menstrual periods
- Reduced libido
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Severe or Untreated Hypothyroidism (Myxedema)
- Extreme fatigue and drowsiness
- Severe swelling (myxedema)
- Slowed speech or movement
- In severe cases, myxedema coma requires emergency medical attention
Diagnostic Testing
To diagnose hypothyroidism, doctors and naturopaths rely on a combination of blood tests and imaging studies to assess thyroid function and identify underlying causes. Key diagnostic methods include:
1. Blood Tests
These tests measure hormone levels to determine if the thyroid is underactive.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test
The most sensitive test for hypothyroidism. High TSH levels indicate an underactive thyroid (primary hypothyroidism). Low or normal TSH with low thyroid hormones may indicate central (secondary) hypothyroidism due to pituitary dysfunction.
- Free Thyroxine (Free T4) Test
Measures the active thyroid hormone circulating in the blood. Low free T4 levels confirm hypothyroidism.
- Triiodothyronine (T3) Test
Usually, this test is not the key test for hypothyroidism, but it may be helpful in certain cases. T3 levels can remain normal even in early hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid Antibody Tests (For Autoimmune Thyroid Disease)
Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase (Anti-TPO) Antibodies: Elevated in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
Anti-Thyroglobulin (TgAb) Antibodies: Also associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders.
- Reverse T3 (rT3) Test (Less Common)
Measures inactive T3 levels and is sometimes used in cases of chronic stress or illness-related hypothyroidism.
2. Imaging Tests
- Thyroid Ultrasound
Used to check for thyroid inflammation, nodules, or goitre. It is often recommended for individuals with lumps or swelling in the neck. - Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAIU) Scan (Rare for Hypothyroidism)
Used if hypothyroidism is caused by thyroiditis or iodine imbalances. - MRI or CT Scan of the Pituitary Gland
Performed if secondary hypothyroidism (caused by pituitary dysfunction) is suspected.
3. Additional Tests (If Needed)
- Cholesterol Panel
Hypothyroidism can cause high cholesterol levels. - Liver Function Tests
Thyroid dysfunction can sometimes affect liver enzyme levels. - Full Blood Count (FBC)
Some people with hypothyroidism may have anemia (low red blood cells).
Interpreting the Results
Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for the interpretation of your results. Results such as in this example may guide ongoing management:
- High TSH + Low Free T4 = Primary Hypothyroidism (Thyroid is underactive).
- High TSH + Normal Free T4 = Subclinical Hypothyroidism (Early-stage, may not need treatment).
- Low or Normal TSH + Low Free T4 = Secondary Hypothyroidism (Pituitary or hypothalamus dysfunction).
- Positive Thyroid Antibodies = Suggestive of autoimmune hypothyroidism (Hashimoto’s Disease).
Naturopathic Approaches to Hypothyroidism
At All Naturopath Surrey Hills, we emphasise individualised care, focusing on natural therapies and lifestyle modifications to restore thyroid function. Key strategies include:
- Nutritional Support: Adequate intake of iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production.
- Herbal Medicine: Herbs such as Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) and Commiphora Mukul (Guggul) have been traditionally used to support thyroid function. These herbs may help modulate hormone levels and improve metabolic rates. It’s essential to consult with a qualified naturopath before starting any herbal regimen.
- Addressing Nutrient Deficiencies: Deficiencies in nutrients like vitamin B12, zinc, and selenium can contribute to an underactive thyroid. Vitamin B12, in particular, assists in improving cellular response and boosting energy production in cells, which can help increase thyroid hormone production. Dietary sources of vitamin B12 include liver, nutritional yeast, various fish, dairy products, chicken, and eggs. Zinc can be obtained from meat, shellfish, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Selenium is essential for thyroid function and can be found in foods like brazil nuts, fish, and eggs.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can adversely affect thyroid function. Incorporating stress-reducing practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can be beneficial. Regular, moderate exercise like walking or swimming also supports overall well-being.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Ensuring adequate sleep, avoiding exposure to environmental toxins, and refraining from smoking are essential steps in managing hypothyroidism naturally. These changes help in reducing symptom severity and promoting hormonal balance.
How can we help?
Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective management. Comprehensive testing, including blood tests to assess thyroid hormone levels and antibody presence, can help identify the underlying cause of hypothyroidism. At All Naturopath Surrey Hills, we offer diagnostic testing to tailor treatment plans to suit your individual needs.
Managing hypothyroidism through naturopathic medicine involves a comprehensive approach that addresses diet, lifestyle, and emotional well-being. By focusing on the body’s innate ability to heal, naturopathy aims to restore balance and improve the quality of life for those affected by hypothyroidism.
ALL Naturopath employs natural therapies to treat hypothyroidism, including nutritional supplementation, herbal medicine and dietary changes. Minerals can replace deficient levels of nutrients necessary for optimal thyroid function and herbal medicine and dietary changes support and encourage an increase in thyroid hormones. If you’re experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism, speak to All Naturopath today.
Call us today at 0402 926 675 for an appointment!
